You may have heard the expression “dermal barrier” or “epidermal barrier” or “skin barrier“, usually in a phrase that mentions how important it is to protect. But what exactly is it?
We will never tire of saying that without proper skin hydration, whatever anti-aging strategy we choose will never be the most effective as possible. The beginning of any effective skincare routine is hydration.
To explain the above, we will need to take a closer look at our skin.
The skin is a basic organ of the human body. Its job is to protect the inside of our body from environmental effects (UV radiation, mechanical effects) but also to prevent harmful compounds from entering our body. At the same time, as we are mainly composed of water, the skin prevents the water inside our body from escaping.

Our skin consists roughly of three major parts: (a) The Epidermis, which is on the surface of the skin (b) Below the epidermis is the Dermis. The dermis contains two important proteins that we have all heard of: Collagen and elastin. Their job is to keep the dermis structure stable and give it elasticity. (c) Deeper is the Subcutaneous adipose tissue. It is practically the ‘insulating material’ between the skin and the internal organs of the body and is extremely important to our lives as it keeps our internal body temperature constant.
Let’s leave the dermis with collagen and elastin for a while and deal with the upper part of the skin, the epidermis. We understand how important is it’s good functionality, as it is our first ‘wall’, the first defense of our body against all the external threats. We want epidermis to allow a sufficient amount of water to enter the body and at the same time not to let the water inside escape. From the individual layers of the skin, we will zoom in on the outer layer (stratum corneum). It’s exactly where we will find the skin barrier.
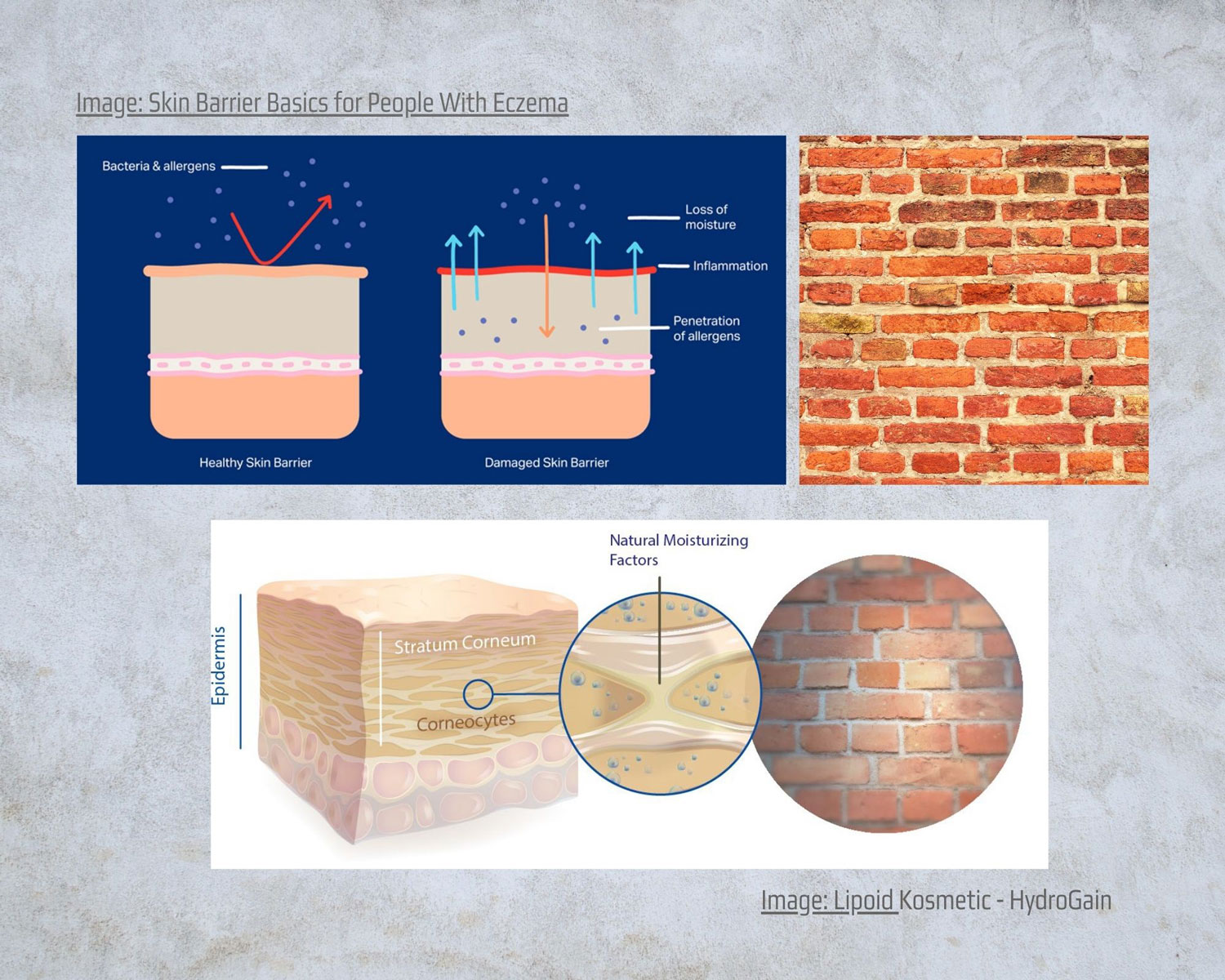
Have you ever played with bricks? Imagine a wall made of bricks, which are connected together with cement.
What are the bricks: Flat keratinocytes, in proximity, surrounded by a protein shell. Another thing that interests us a lot is that inside the bricks (between the keratinocytes) there are specific amino acids (NMF = Natural Moisturizing Factors), whose job is to “hold” water.
What is cementum: The “cementum” between keratinocytes is lipids. Lipids are hydrophobic by nature. They are afraid of water, so they keep it “away” from them, that is, inside our skin, without letting it leave us.
From all the above we understand the great importance of the skin barrier and the big role it plays for the complete and holistic hydration of our skin. Can we enhance its action with our cosmetic treatment?
An ideal holistic hydration approach would target the following points:
(a) Transport of water throughout our epidermis including its deeper layers.
(b) Reinforce the proteins (bricks) and lipids (cement) of the skin barrier so that they do not let water escape.
(c) Increase in the number of amino acids (NMF) which, as we saw above, they retain water.
This is the reason that we choose HydroGain active material as the star component of our Helios serum.